critical thinking mental health NCLEX review 1
Yura Casanas Gonzalez: MSN/RN/MD (foreign)
Mamografías e investigaciones a bajo costo y gratis (cáncer de mamas)
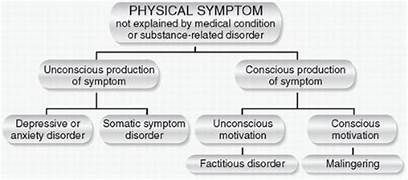
Somatic symptom disorder. Somatic symptom disorder is characterized by physical symptoms that cannot be explained by a physical disorder. The client comes to the nurse's station and reports chest pain. The nurse knows this is a new symptom for the client, in a similar case the nurse should assess the patient, reassuring, without judge them.
The type and frequency of symptoms in somatization disorders differ depending on the culture
in which they are expressed. For example, there is a higher reported frequency of somatization disorder in Greek and Puerto Rican men than in men in the United States. Therefore, the symptoms reported could be linked to the cultural beliefs and values.
Factitious disorder, also known as Munchausen syndrome, is characterized by the
conscious fabrication
of symptoms or self-inflicting injuries
to gain attention.
Clients who have factitious disorder can have multiple hospitalizations or even surgeries as a manifestation of this disorder.
Patient with factitious disorder has unexplained pain
Clients who have factitious identity disorder can experience unexplained abdominal pain, surgeries, bleeding, fever, hypoglycemia, seizures, or cancer, which can be manifestations that are manufactured or self-inflicted.
The neurological symptom disorder often worses or becomes more apparent when a client is experiencing a stressful situation.
Statement response by the health professional or nurse: "We will work with you to help you develop ways to manage your symptoms that are caused by the disorder"
Functional neurological disorder, also called conversion disorder, is characterized by neurological manifestations that have no neurologic cause.
Autistic Spectrum disorder: A nurse can act as an advocate for a client in coordinating care, education, and skill development with counselors, teachers and school staff to promote good outcomes.
Young children who have ASD often exhibit restricted, repetitive patterns of behavior, interests, or activities. This may include repeating the words and actions of others without reason or context.
A client with a
stereotypical motor disorder would have difficulty controlling impulsive movements when excited, so a good outcome statement to evaluate progress of interventions would be to control these movements effectively. Young children who have ASD often exhibit restricted, repetitive patterns of behavior, interests, or activities. This may include repeating the words and actions of others without reason or context.
Advocacy also includes talking to the provider about changing the dose of medication or switching to a different medication to decrease negative effects.
Completing homework requires attention and mental effort.
The nurse should then discuss behavioral interventions with the guardian when implementing interventions for addressing the child’s behaviors at home and school
Tourette: multiple motor tics and one or more vocal tics many times throughout the day for 1 year or more
Conduct disorders risk factors and symptoms: School history of negative behavior (being impulsive) , aggressive treatment to animals, parental history of neglect, bipolar disorder, conduct disorders, and substance use, living or family dysfunction that include a
history of frequently running away from home and now having no permanent home, and displaying disregard in interactions with other clients are all indications of conduct disorder that have led the client, as an adult, to display manifestations of antisocial personality disorder.
Behavioral disruptive disorders are a group of disorders linked to difficulty in self-control and aggressive behavior toward others.
Conduct disorders .
The nurse should first address the client's safety, followed by their refusal to take their medications.
Clients who have intermittent explosive disorder, frequently have impulses that result in explosive rage that is disproportionate to the situation. These rage explosions can be dangerous and destructive in nature and can cause injury to the client or others.
Oppositional defiant disorder (ODD)
is a disruptive behavior disorder appearing during
childhood or
adolescence and frequently is given by
persistent angry or irritable mood, unruly and argumentative behavior, and intention to seek revenge (vindictiveness). It frequently manifests in hostility toward authority figures
Reporting the breach of confidentiality upholds the ethical and legal obligation to protect client privacy.
Establishes boundaries:
The nurse should clarify the boundaries
refocusing
the client back to the issue of the session. Avoid options that may be judgmental and may provide an opening for a verbal struggle or those that are a social response and could be misinterpreted by the client.
Delirium risk factors: Include increased severity of physical illness, older age, and baseline cognitive impairment such as that seen in dementia. Delirium usually develops over a short period, rapid onset, throughout the course of a day. An older adult client with sepsis is at the highest risk for the development of delirium due to the seriousness of the illness. It is typically a direct physiological consequence of another medical condition, substance intoxication or withdrawal, exposure to a toxin, or multiple etiologies.
Alzheimer:’s disease: Affected executive function including planning, decision making, and working memory.The nurse should identify a client who has Alzheimer's disease and is having difficulty multitasking is experiencing a cognitive deficit of executive function, memory loss that affect daily activities progressively (ADLs)
Impaired attention, memory, and abstract thinking: cognitive disorder
references: Videbeck. LS (8ed) Kluver, W (2023) Physichiatry mentalhealth/nursing.